Ever opened your Amazon Web Services bill and wondered why it was higher than expected? You’re not alone. Many businesses find that AWS data transfer costs are a significant part of their cloud costs. They often catch them by surprise.’
These fees occur when you move data into, out of, or within the Amazon Web Services network. The cost depends on your location, the source and destination of the data, and the services you use, as well as the amount of data being transferred. This guide addresses a crucial but often overlooked aspect of cloud billing.
AWS Data Transfer Pricing Models Explained
Data transfer pricing on AWS follows a multi-tiered approach. It accounts for both infrastructure costs and market conditions across different global regions. This pricing model determines how much you pay to move data in and out of Amazon’s cloud services. Understanding these models helps you plan your cloud architecture and budget more effectively.
Ingress vs. Egress Pricing Structure
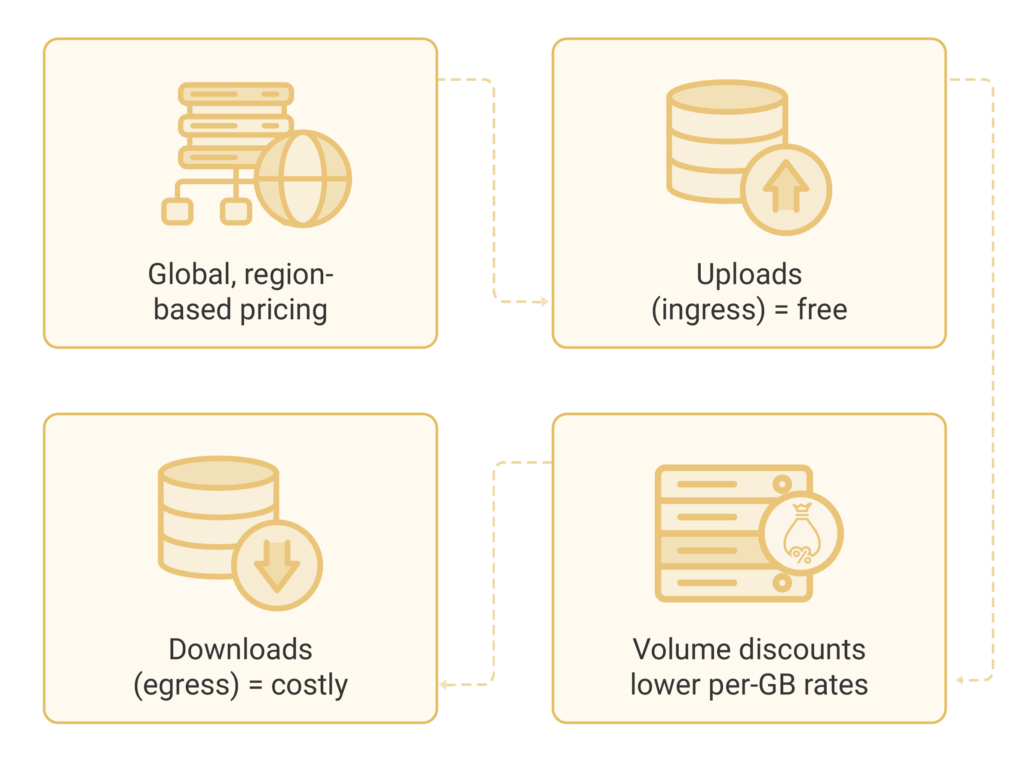
AWS has an asymmetrical pricing model. Data transfer into all AWS regions from the Internet is completely free. This means you never pay for uploading data, files, or content to AWS services from external sources.
However, egress transfers have different rules. When you move data out of AWS to the Internet, you are charged based on regional rates. This pricing strategy encourages migration to AWS while generating revenue from data usage.
The asymmetrical structure benefits businesses during initial cloud adoption. You can upload large datasets without worrying about transfer costs. However, you need to plan carefully for ongoing data distribution needs.
Regional vs. Global Transfer Rates
AWS bandwidth pricing varies across different geographic regions. Each region has its own rate structure that reflects local infrastructure costs and market conditions. For example, Asia Pacific regions typically charge higher rates than US-based regions for the same data volumes.
Inter-region data transfer costs depend on both the source and destination locations. Moving data between US East and US West regions costs less than transferring the same amount between US East and Asia Pacific regions. These rate differences can impact your architectural decisions when designing multi-region deployments.
Global transfer rates apply when you need to move data across continents or between distant regions. Planning your regional strategy is essential for managing these costs.
Tiered Pricing and Volume Discounts
AWS implements a tiered pricing structure. This structure rewards higher usage volumes with lower per-GB rates. Your monthly data transfer costs decrease as you move through different usage tiers within each billing period.
The tiered system works progressively throughout each month. Your first 10TB of egress typically costs more per GB than usage beyond 150TB. This approach makes AWS more competitive for enterprises with substantial data transfer requirements.
| Usage Tier | Monthly Volume | Rate per GB (US Regions) | Rate per GB (Asia Pacific) |
| Tier 1 | First 10TB | $0.09 | $0.114 |
| Tier 2 | Next 40TB | $0.085 | $0.098 |
| Tier 3 | Next 100TB | $0.07 | $0.092 |
| Tier 4 | Over 150TB | $0.05 | $0.089 |
Source: Amazon EC2 pricing.
Types of Data Transfer in AWS
Data transfer in AWS has different types, each with its own pricing and data transfer optimization chances. Your cloud setup affects which types you use most. These types help AWS figure out your monthly data charges.
Each type meets different business needs and has its own cost. Knowing these differences helps you plan your resources and data flow better.
1. Internet Data Transfer
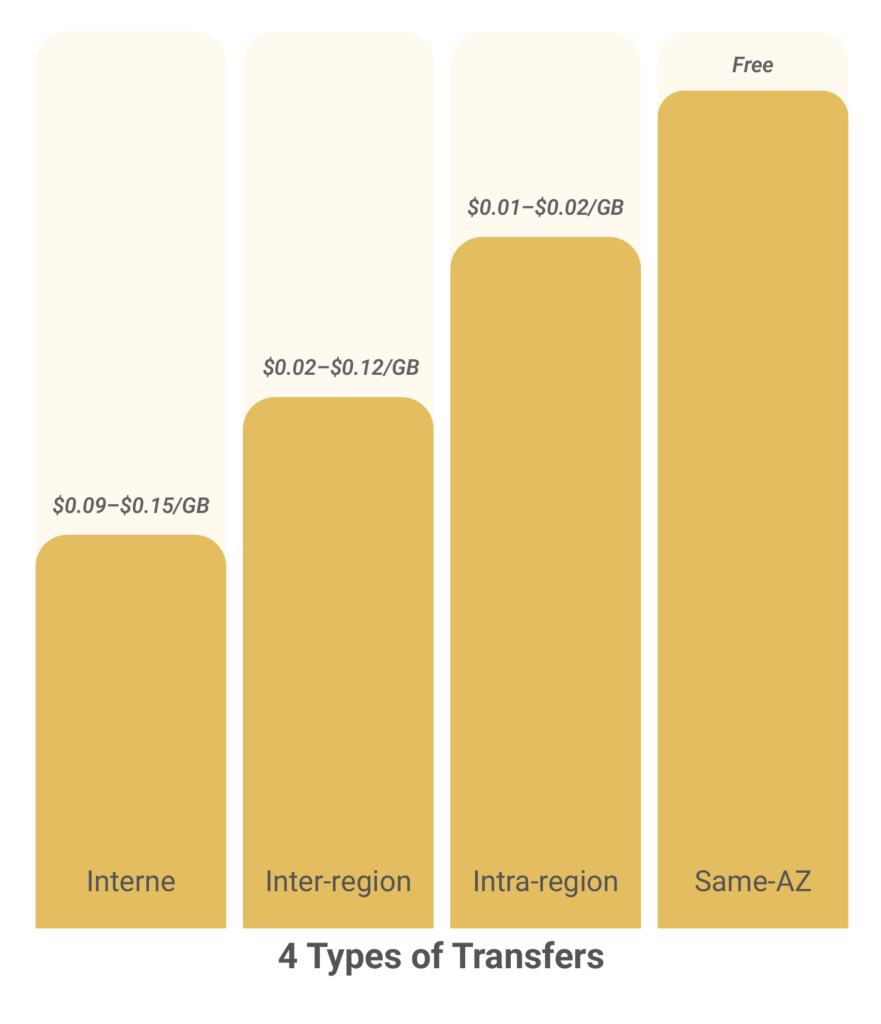
Internet data transfer is the most expensive in AWS. It covers all traffic between your AWS resources and outside users or systems. Web applications that serve content to visitors use the highest internet transfer volumes. Common scenarios include API responses, file downloads, and streaming media delivery. Costs range from $0.09 to $0.15 per GB, depending on your region.
2. Inter-Region Data Movement
Inter-region transfers occur when data is moved between AWS regions for disaster recovery or global access. AWS charges specific fees for these transfers. Cross-region database replication is a major cost factor.
3. Intra-Region Transfer Scenarios
Intra-region transfers occur within the same AWS region, across zones or services. They are more cost-effective than internet or inter-region transfers. Availability zone transfer costs can add up in distributed setups. Examples include load balancer traffic and cross-AZ database sync.
| Transfer Type | Cost Range (per GB) | Common Use Cases | Optimization Priority |
| Internet Transfer | $0.09 – $0.15 | Web traffic, API calls, downloads | High |
| Inter-Region | $0.02 – $0.12 | Disaster recovery, global distribution | Medium |
| Intra-Region | $0.01 – $0.02 | Cross-AZ communication, load balancing | Low |
| Same-AZ | Free | Local service communication | Architectural |
Source: Amazon Data Transfer EC2
AWS Services and Their Transfer Costs
Each AWS service has its own way of handling data transfer costs. This affects your cloud costs. Understanding these costs is necessary in managing your AWS cost management strategy.
Some services, like DynamoDB, SQS, and SNS, charge differently for data moving between regions. This can make your cloud setup more expensive if not planned well.
1. Amazon EC2 Data Transfer Charges
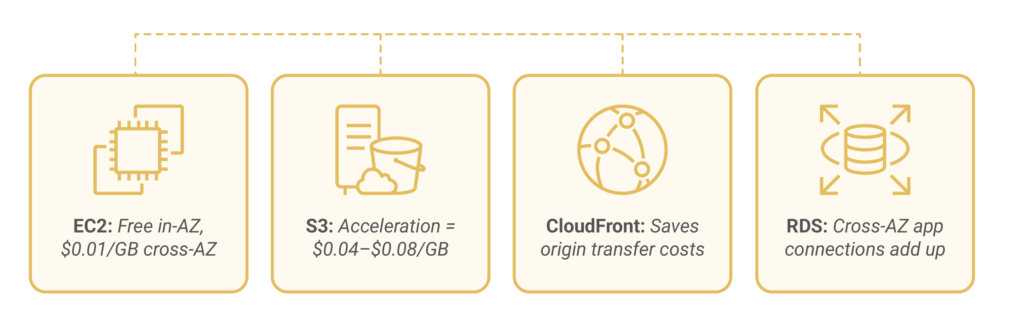
Amazon EC2 data transfer costs are predictable and can be optimized. No charges apply for data moving within the same availability zone using private IP. However, moving data across zones costs $0.01 per GB in each direction.
2. Amazon S3 Transfer Pricing
Amazon S3 has complex pricing that goes beyond standard rates. S3 Transfer Acceleration costs $0.04-$0.08 per GB for faster transfers. Different storage classes also have different transfer costs.
3. CloudFront and CDN Distribution Costs
CloudFront pricing varies by edge location. It reduces origin transfer costs through caching but has its own pricing. It’s cost-effective for global users and high-content access.
CloudFront is worth it for certain usage patterns. It’s good for global distribution and frequent content requests, reducing server loads.
4. RDS and Database Transfer Fees
Amazon RDS and database services have unique transfer pricing. Multi-AZ deployments don’t incur charges for replication, but cross-AZ app connections do. Your database setup greatly affects cloud networking costs. Cross-AZ app connections quickly add up, and backup strategies require careful cost planning.
Hidden Data Transfer Costs You Need to Know
AWS has hidden charges that can affect your cloud budget. These costs are often hidden in other service fees.
1. NAT Gateway Transfer Charges
NAT Gateways can lead to hidden costs in AWS. They charge $0.045 per gigabyte for data processing, on top of internet egress rates.
This means your internet traffic costs almost double. For example, 100 GB monthly through a NAT Gateway results in extra fees.
2. Load Balancer Data Processing Fees
Application and Network Load Balancers have extra fees. These fees apply to all traffic, including health checks and internal communication.
High-traffic apps can face big processing charges. Fees range from $0.008 to $0.022 per gigabyte, depending on the load balancer type and setup.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Data Transfer
Effective network cost reduction strategies can lower your AWS data transfer expenses, helping your system run smoothly. It’s all about planning and applying the right practices in your cloud setup. Focus on three key areas for maximum savings. Each strategy is helpful on its own, but they work best together. Let’s explore how to reduce data transfer costs effectively.
Architectural Design for Cost Efficiency
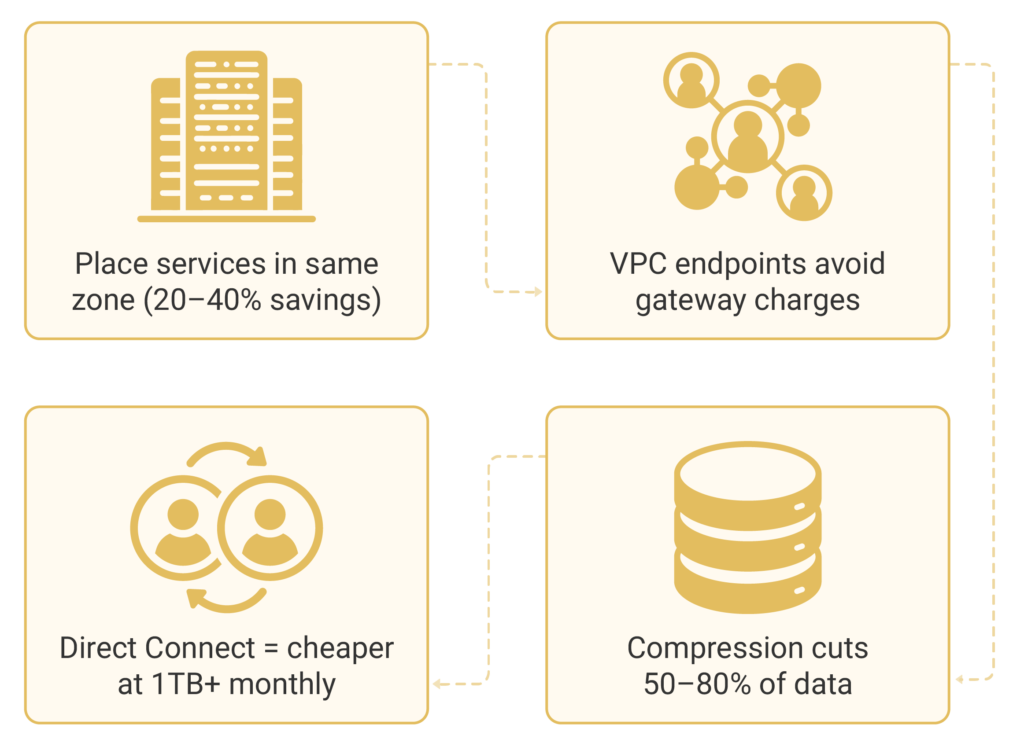
AWS architecture optimization begins with smart resource placement. This means putting related services in the same zone to avoid extra charges. This simple step can cut costs by 20-40% for apps that talk to each other a lot.
Use VPC endpoints for AWS services to avoid internet gateway costs. These endpoints give direct access to services like S3 and DynamoDB without data leaving your VPC, which can save a lot of money, especially for big data users.
For on-premises connections, use AWS Direct Connect instead of the internet. It provides predictable pricing and can be more cost-effective for large data transfers. It’s best for those transferring over 1TB of data each month.
Data Compression and Optimization Techniques
Data compression can cut transfer volumes by 50-80% without changing your setup. Use gzip, brotli, or other algorithms at the app level. This is great for text data, logs, and API responses.
Make your data formats and sizes smaller to save on costs. Use formats like Protocol Buffers or MessagePack instead of JSON or XML. Also, optimize database queries and filter results to reduce costs in distributed systems.
Take Control of Your AWS Data Transfer Costs
Managing AWS costs can feel overwhelming, especially when hidden transfer fees start eating into your budget. Don’t leave savings on the table. Elite Cloud’s free cost assessment helps you uncover inefficiencies, identify underutilized resources, and cut unnecessary spending.

Contact Elite Cloud today and start confidently optimizing your AWS costs.




