What Is a CDN?
CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a globally distributed network of servers designed to accelerate the delivery of both static and dynamic content.
Instead of forcing users to connect directly to your origin server, a CDN caches your website’s resources across servers located closer to your users.
Core Functions of a CDN
- Improve website loading speed: CDNs cache static assets — such as images, CSS, and JavaScript — across multiple global nodes to reduce response time and improve page load speed.
- Balance server load: By intelligently managing and distributing traffic, CDNs prevent single-server overloads that could slow down or even crash your website.
- Enhance global availability: With multiple edge nodes worldwide, a CDN ensures consistent performance across all regions. Many edge nodes can even perform light compute tasks, reducing the origin server’s load by up to 50%.
- Strengthen security: Modern CDNs come with built-in DDoS protection, Web Application Firewall (WAF), and SSL encryption, keeping your website safe and stable.
When Should Businesses Use a CDN?
✅ Recommended for:
- Websites that need faster loading times and better user experience.
- Businesses serving a global audience and need to reduce cross-border latency.
- High-traffic websites looking to offload their servers and cut bandwidth costs.
❌ Not ideal for:
- Low-traffic sites with users concentrated in a single region.
- Sites with highly dynamic, uncachable content.
CDN Explained with a Simple Analogy
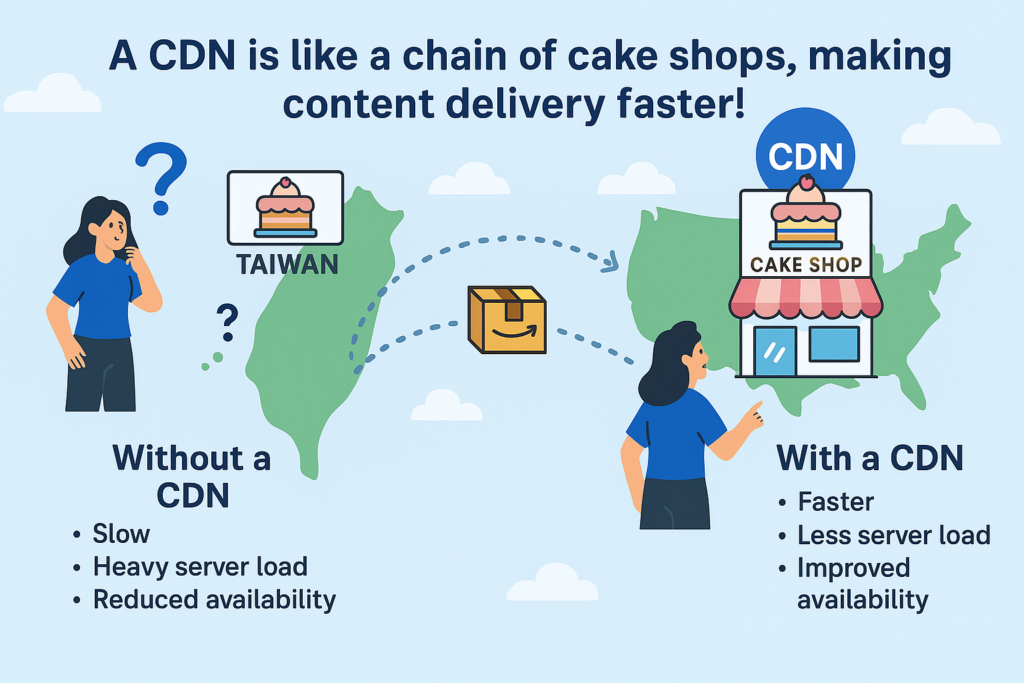
If your favorite bakery is in the US but you live in Taiwan, every time you order a cake it must travel thousands of kilometers — taking more time, costing more, and possibly ruining the quality. That’s what happens to a website without a CDN: every user request goes directly to a distant origin server, causing high latency, slow loading, and heavy server load.
If the bakery opened branches around the world — CDN edge locations (PoPs) — and stocked them in advance, you could simply buy from the nearest store in Taiwan. Faster, easier, and far more convenient.
That’s exactly how a CDN works. It caches your website’s content across multiple edge locations worldwide, allowing users to fetch resources from the closest server instead of making a long round trip back to the origin. This speeds up loading times, reduces latency, and significantly lowers the burden on your origin infrastructure.
That’s exactly how a CDN works. It caches your website’s content across global edge locations so users can retrieve data from the nearest server without returning to the distant origin. The result: faster load speeds, reduced latency, and lighter origin workload.
How CDNs Improve Global Access Speed and Stability
Reduce latency by minimizing physical distance
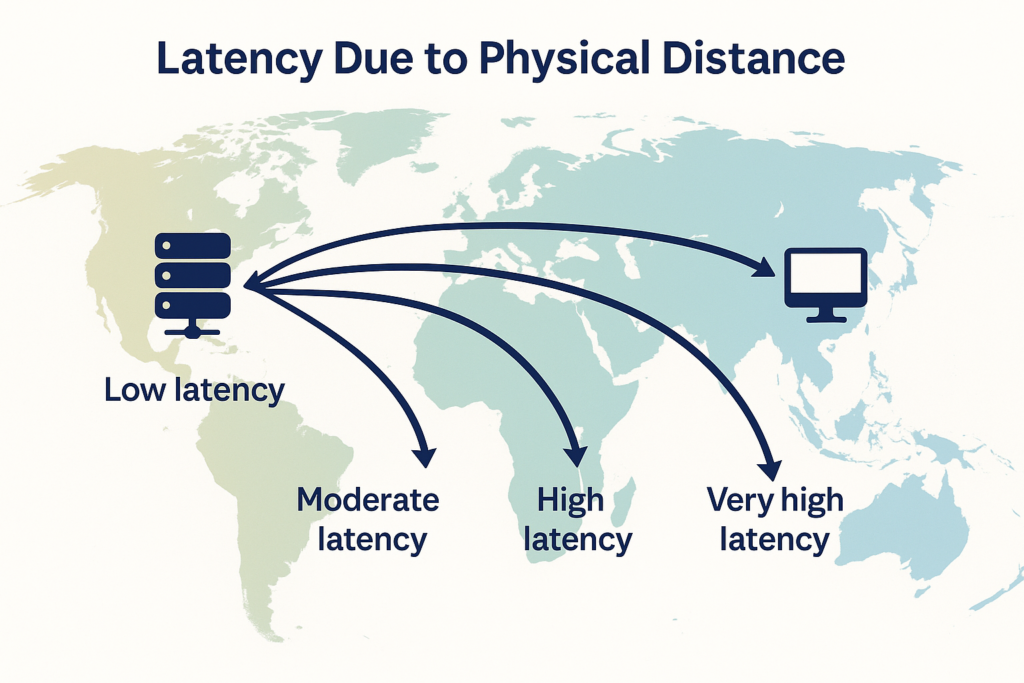
Many businesses start by relying on a single server to deliver all website content. But as traffic grows and users spread across different regions, physical distance becomes a major factor affecting loading speed and overall user experience.
When a user sends a request, the data must travel from the origin server to the user’s device.
The farther the distance, the more network hops the request must pass through — resulting in higher latency.
| Distance | Pure Fiber Transmission Time (Theoretical) | Actual Network Latency (RTT, including routing) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 km | ~0.5ms | ~5ms |
| 1,000 km | ~5ms | ~15-30ms |
| 5,000 km (Mainland China to the US) | ~25ms | ~80-150ms |
| 10,000 km (Asia to the US) | ~50ms | ~150-250ms |
| 20,000 km (Europe to Australia) | ~100ms | ~200-400ms |
A CDN distributes static content across its global edge locations (PoPs), caching files on servers closer to users. This eliminates the need for long-distance retrieval from the origin and can reduce latency by 50% to 80%.
Take Netflix 4K streaming as an example:
When an Asian viewer accesses a US-based server without a CDN, the load time is typically around 8–10 seconds. With a CDN caching the video at a nearby edge location, the load time drops to 1–2 seconds, dramatically improving playback smoothness and minimizing buffering.
Reducing Origin Load for Stable High-Traffic Performance
A CDN boosts more than just speed — it also significantly reduces the load on your origin server, ensuring stable performance even during sudden traffic spikes.
Below is a comparison of server load with and without a CDN:
| Test Environment | Without CDN (Origin Load) | With CDN (Reduced Load) | Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| News website (5M daily views) | 5000 req/sec | 1000 req/sec | ↓ 80% |
| eCommerce site (peak sales, 2000 orders/sec) | 2000 req/sec | 800 req/sec | ↓ 60% |
| Streaming platform (4K playback) | 50 Gbps | 5 Gbps | ↓ 90% |
| Online game (real-time API) | 200 ms TTFB | 50 ms TTFB | ↓ 75% latency |
In real-world cases, CDNs can cut 50–90% of server load, ensuring consistent performance while lowering bandwidth and infrastructure costs.
Use Cases and Industries That Benefit from CDNs
Industries That Benefit from CDNs
eCommerce:
- Faster page and image loading improves conversion rates.
- Handles heavy traffic during peak campaigns like Singles’ Day or Black Friday.
Media streaming:
- Ensures smooth playback and adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR).
- Adjusts video quality automatically based on user bandwidth.
Gaming:
- Caches updates and patches to speed up downloads.
- Reduces latency for multiplayer games, enhancing player experience.
How to Choose the Right CDN Provider
When evaluating CDN providers, businesses should consider global reach, performance, security, pricing, and integration capabilities. Different vendors excel in different areas — from caching and edge computing to DDoS protection and dynamic acceleration.
Below are the key evaluation criteria (see table):
| Evaluation Criteria | Description | Recommended Providers |
| Global Coverage | Number and distribution of PoPs worldwide | Akamai、Cloudflare、AWS CloudFront |
| Performance (Latency & Load Optimization) | Ability to optimize dynamic and cached content delivery | Fastly, Google Cloud CDN, Cloudflare |
| Security (DDoS, WAF) | Built-in DDoS mitigation, WAF, and Zero Trust controls | Cloudflare, Akamai, AWS CloudFront |
| Cloud Integration | Seamless integration with AWS, Google Cloud, Azure | AWS CloudFront, Google Cloud CDN, Azure CDN |
| Edge Computing | Support for serverless edge functions and compute at the edge | Akamai Edge Compute, Cloudflare Workers, Fastly Compute |
| Pricing Flexibility | Scalable pricing models for businesses of different sizes | BunnyCDN, Cloudflare, Fastly |
| Regional Focus | Optimized infrastructure for specific markets (e.g., China, Southeast Asia) | Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud |
Conclusion
A CDN plays a vital role in improving website performance, reducing latency, offloading servers, and strengthening security — making it an essential technology for modern businesses.
Leading CDN providers like Akamai, Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, Fastly, Google Cloud CDN, Alibaba Cloud, and Tencent Cloud each bring unique advantages. The right choice depends on your business needs, regional coverage, and integration requirements.
At Elite Cloud, we partner with major cloud providers — including AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud — to deliver custom CDN deployment, optimization, and cloud integration services.
We help businesses design the most efficient CDN architecture to ensure the fastest, most secure global access experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Does using a CDN affect my website’s SEO performance?
- Yes — in a positive way. A CDN improves page loading speed, and Google treats site speed as a major ranking factor.
- In addition, CDNs support secure HTTPS connections, which is also considered an SEO best practice recommended by search engines.
2. Is every website suitable for using a CDN?
- Most websites benefit from a CDN — especially eCommerce stores, video platforms, news media, gaming services, and SaaS applications with higher traffic volumes.
- However, if your site has very low traffic and targets users in a single region, local hosting may already be sufficient and the benefits of a CDN may be limited.
3. Does a CDN require ongoing maintenance or frequent configuration?
- Not much. CDNs automatically handle caching, routing, and traffic distribution.
- The only time you may need manual action is when your website updates its content — in that case, you might need to purge the cache to ensure visitors see the latest version immediately.
4. How does a CDN improve website security?
- A CDN strengthens security with built-in DDoS protection, Web Application Firewall (WAF), and SSL/TLS encrypted connections.
- It can also hide your origin server’s IP address, reducing the risk of targeted attacks.
5. Does using a CDN increase operational costs?
- It depends on your traffic and the plan you choose. Some CDN providers — like Cloudflare Free — offer free tiers suitable for small websites.
- High-traffic websites may require paid plans, but a CDN can reduce origin load and bandwidth usage, which often leads to lower infrastructure costs over time.



