Conversational AI has revolutionized the way businesses interact with customers, making support more accessible, efficient, and user-friendly. Amazon Lex, a fully managed AI service for building conversational interfaces, allows developers to create chatbots with ease. In this hands-on guide, we will demonstrate how to build a simple SupportBot using Amazon Lex.
What is Amazon Lex?
Amazon Lex is a cloud-based service that enables developers to build and deploy chatbots for text and voice interactions. Powered by the same deep learning technologies as Amazon Alexa, Lex simplifies natural language understanding (NLU) and allows for seamless integration with other AWS services.
Use Case: SupportBot
We will build a SupportBot, a customer service chatbot that helps users with common support queries, including:
- Password resets
- Order tracking
- Login issues
- General inquiries
- Human support requests
This chatbot will be designed using Amazon Lex, and all responses will be static (predefined). This keeps the setup simple and ideal for demonstrations.
Setting Up Amazon Lex
Before we start building our chatbot, ensure that you have the following:
- An AWS account (Sign up at AWS Console).
- IAM permissions for Amazon Lex.
Step 1: Create a Lex Bot
First log in to the AWS Management Console and search for Amazon Lex.
Navigate to Amazon Lex. Then click Create bot.
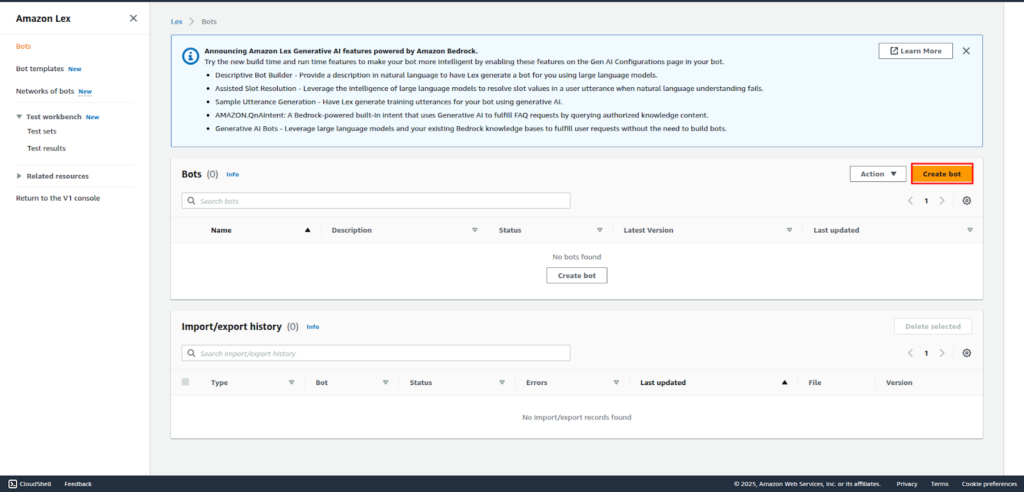
Select Create a blank bot from the Traditional option and provide a name (e.g., “SupportBot“).
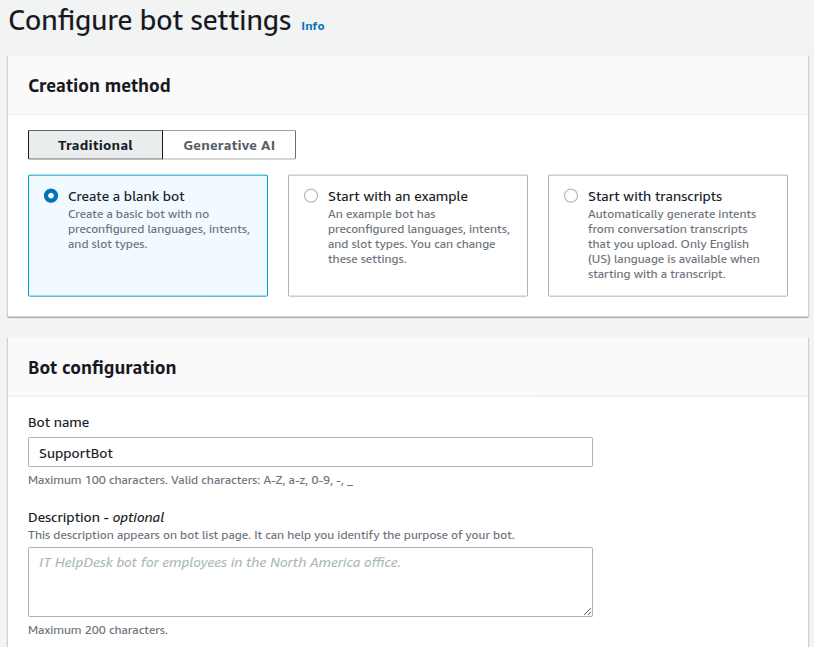
Select Create a new IAM role to allow Lex to operate.
Choose No for the COPPA Compliance (unless you’re building for children). Then configure the rest of the options and Click Next to proceed.
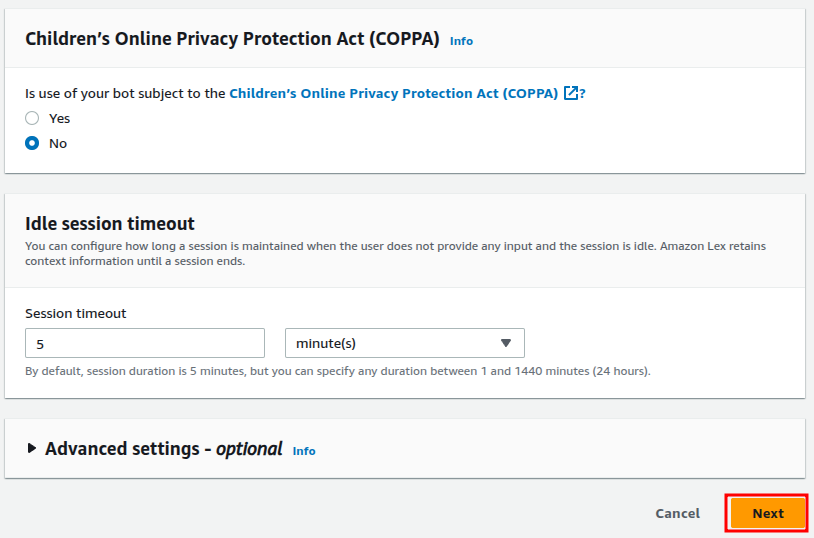
Select a language and a voice interaction model according to your needs and modify other parameters. And then select Done.
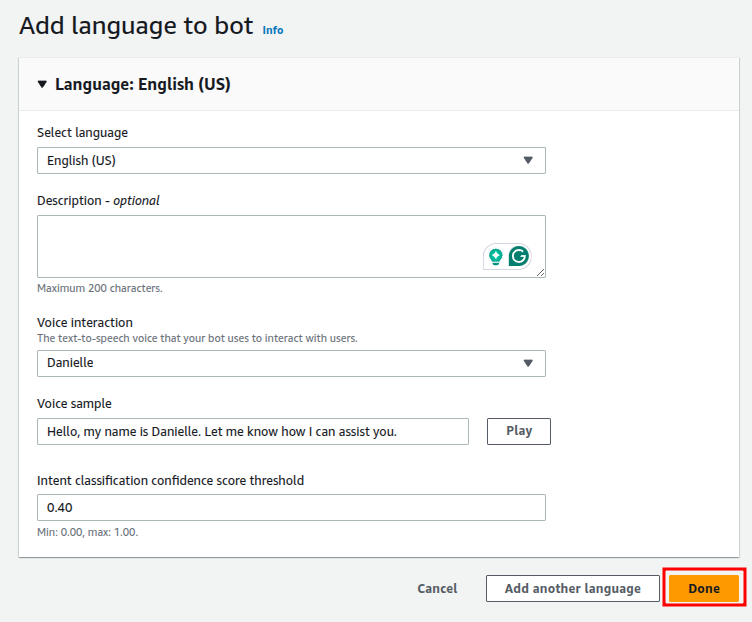
Step 2: Define Intents
An intent represents an action the chatbot can handle. We’ll define five intents with predefined responses. After the previous stage, it would automatically redirect you to the intent page if not then click Add Intent from the bot page.
Note: We will define one intent (PasswordResetIntent) in detail as an example. You can follow the same process to create additional intents.
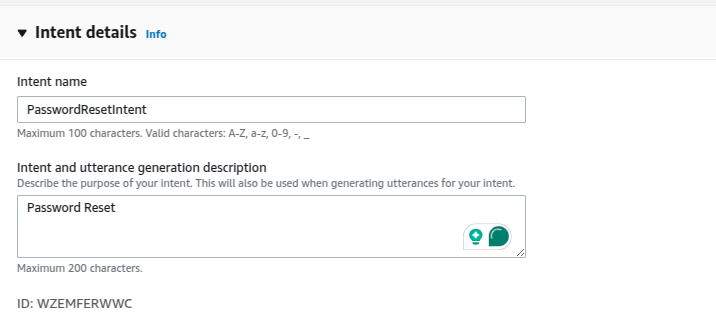
1. Password Reset Intent
Select the intent name, we’re going to name it PasswordResetIntent
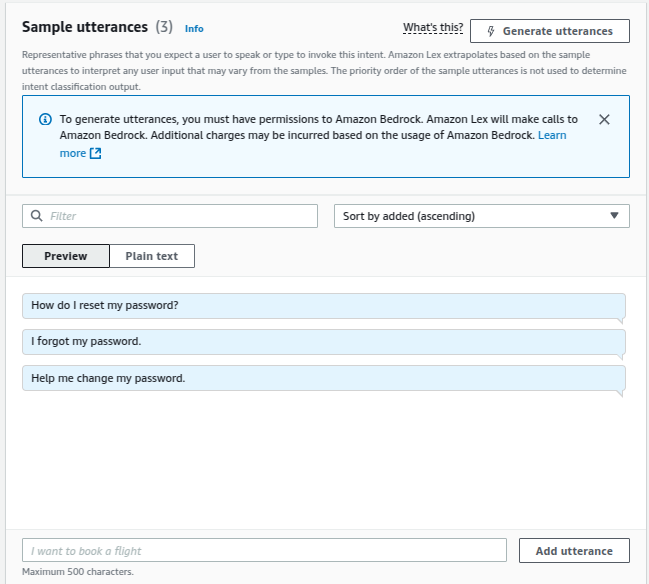
Utterances are the different ways a user might express a request to a chatbot. For the sample chatbot, usual password reset utterances could be:
- “How do I reset my password?”
- “I forgot my password.”
- “Help me change my password.”
Then add the following Response that will respond to the user in case the intent gets triggered:
- “You can reset your password by visiting the password reset page on our website.”
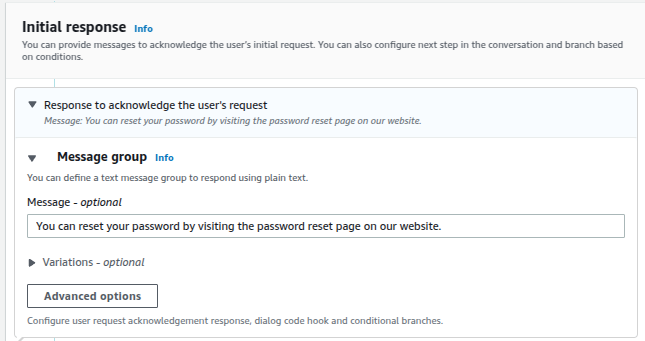
Click on the Save Intent button. Repeat the process for other intents.
2. Order Tracking Intent
- Intent Name: OrderTrackingIntent
- Sample Utterances:
- “Where is my order?”
- “Track my order.”
- “Has my order shipped?”
- Response:
- “Please visit the order tracking page and enter your order ID to check the status of your order.”
3. Login Issues Intent
- Intent Name: LoginIssuesIntent
- Sample Utterances:
- “I can’t log in.”
- “Login not working.”
- “Why am I locked out?”
- Response:
- “Try clearing your browser cache and ensure you’re using the correct credentials. If the problem persists, contact support.”
4. General Inquiry Intent
- Intent Name: GeneralInquiryIntent
- Sample Utterances:
- “Tell me about your services.”
- “What do you offer?”
- “How does this work?”
- Response:
- “We offer a range of products and services. Visit our website for more details!”
5. Human Support Request Intent
- Intent Name: HumanSupportIntent
- Sample Utterances:
- “I want to talk to a human.”
- “Connect me to support.”
- “Live agent please.”
- Response:
- “You can contact our support team via email or phone. Visit our support page for details.”
Step 3: Build and Test the Chatbot
Go to the intent page and review your intents then click Build to compile the chatbot.
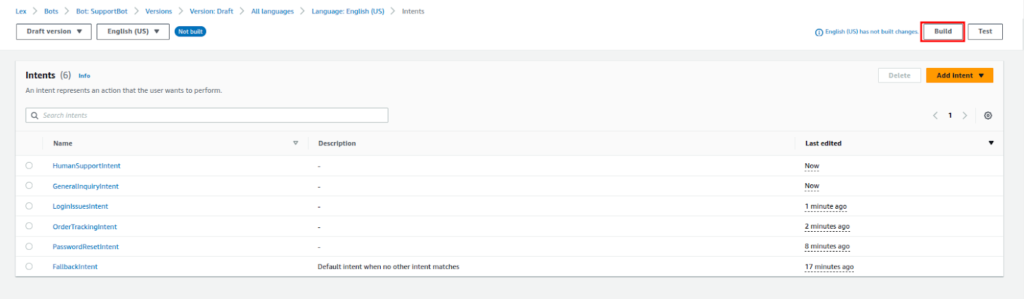
Once built, click on the Test button right next to the built button.
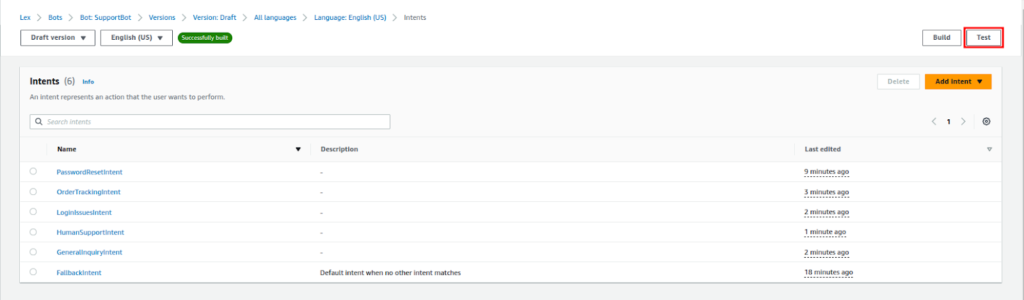
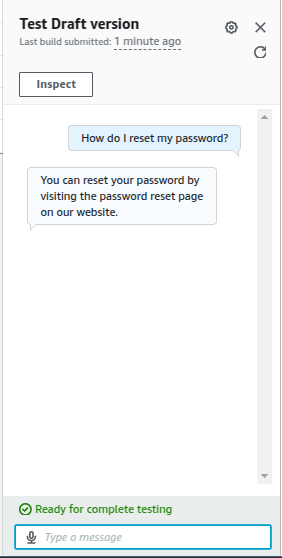
Enter test queries (e.g., “How do I reset my password?”) and verify responses.
Step 4: Deploy the Bot (Optional)
Once tested, you can integrate SupportBot with various platforms to make it accessible to users. Some common deployment options include:
- Amazon Connect – For handling voice interactions.
- Slack, Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp – To provide automated support on messaging platforms.
- Website Chat Widget – Embedding the chatbot on your website for instant customer assistance.
However, deploying the bot is out of scope for today’s tutorial. Our focus has been on building and testing a simple chatbot within Amazon Lex without external integrations.
Amazon Lex
Serverless chatbots can scale, but so can their bills if not configured right. Elite Cloud helps you build efficient Lex bots that minimize idle usage and reduce response costs.
Consult with us to design conversational AI with budget in mind.
Conclusion
Amazon Lex makes it incredibly easy to build conversational AI chatbots without writing complex machine learning code. In this hands-on guide, we created a SupportBot that handles customer queries with predefined responses. This setup is great for demonstrations, but for production, you can integrate AWS Lambda to fetch real-time data, authenticate users, and perform backend operations.
FAQs
What is Amazon Lex used for?
Amazon Lex is a service for building chatbots that support text and voice interactions. It powers customer support, voice apps, and automated assistants with ease.
Do I need coding skills to use Amazon Lex?
Not necessarily. You can create bots using a visual interface and predefined responses, making it beginner-friendly while still supporting advanced logic via AWS Lambda.
Can I deploy Lex bots on multiple platforms?
Yes, Amazon Lex integrates with Slack, Facebook Messenger, websites, and even voice platforms like Amazon Connect for broad deployment options.
What are intents in Amazon Lex?
Intents are user goals or requests (like password resets or tracking orders). You define sample utterances and responses to handle each intent effectively.
Is Amazon Lex suitable for production?
Absolutely. While this guide shows a simple setup, Lex supports dynamic responses through Lambda and scales easily for enterprise-level use.




