Serverless computing transforms how we build applications by eliminating server management tasks. However, AWS Lambda cost can quickly become a budget problem if not planned carefully. To manage Lambda costs well, you need to understand the pricing factors before starting.
Understanding AWS Lambda Pricing Model
To understand the Lambda pricing model, you need to know three main components. AWS calculates your costs by summing request volume, function duration, and memory usage. This clear pricing ensures you only pay for what your functions actually consume.
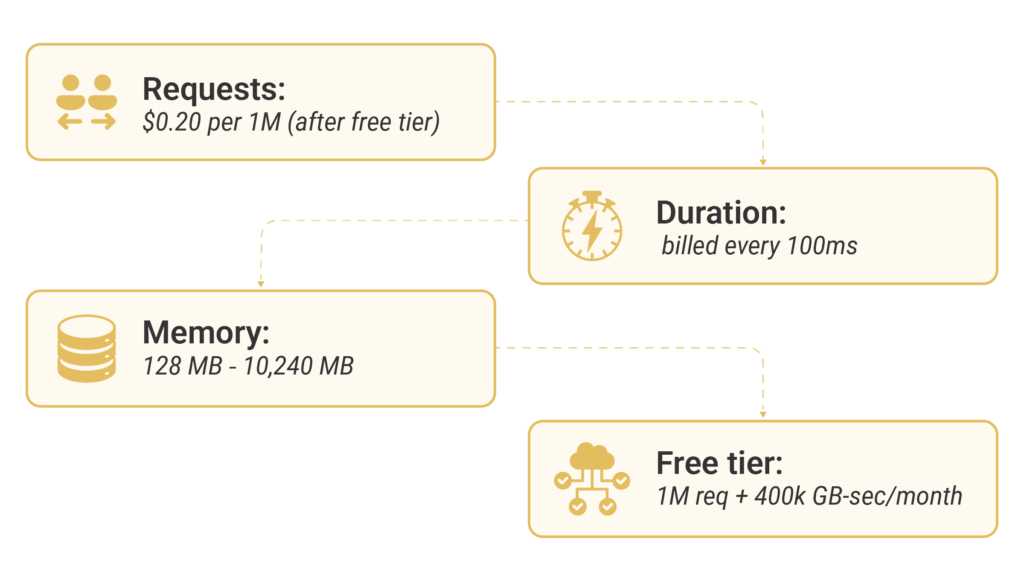
Request-Based Pricing Structure
AWS charges for every function call, regardless of its duration. You are billed per million requests, with costs starting at $0.20 per million after surpassing the free tier.
Duration and Memory Allocation Costs
Memory allocation costs are the main factor in Lambda’s pricing. AWS charges for compute time every 100 milliseconds. This depends on how long your function runs and the amount of memory it uses. You can select memory from 128 MB up to 10,240 MB. Using more memory can give your function more power, which might make it run faster and save you money in the long run.
| Architecture | Duration | Requests |
| x86 Price | ||
| First 6 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.0000166667 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
| Next 9 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.000015 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
| Over 15 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.0000133334 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
| Arm Price | ||
| First 7.5 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.0000133334 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
| Next 11.25 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.0000120001 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
| Over 18.75 Billion GB-seconds / month | $0.0000106667 for every GB-second | $0.20 per 1M requests |
Source: AWS Lambda Pricing – Region US East Ohio (Accessed September 2025)
Free Tier Benefits and Limitations
AWS offers a free tier to help reduce your costs initially. You receive 1 million free requests and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time each month. These limits reset every month and apply to all your Lambda functions.
1. Memory Optimization Strategies
Your function’s memory setting affects both CPU power and costs. This makes choosing the right memory size very important for saving money.
Memory allocation directly affects your Lambda bills because AWS charges based on memory size and execution time. More memory increases costs per second but can also speed up your function.
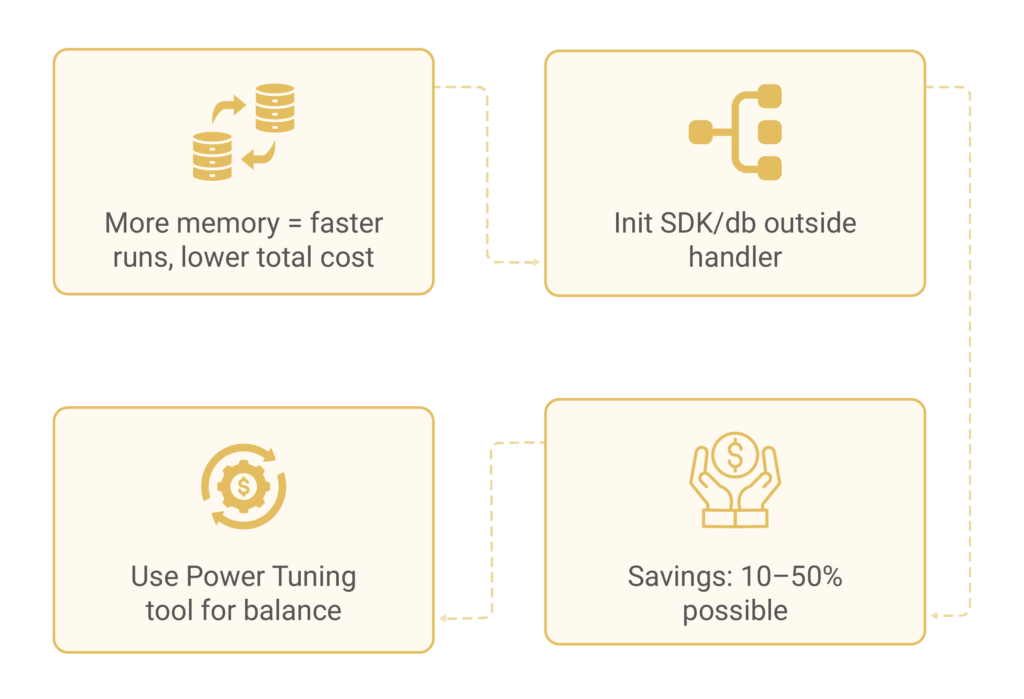
Right-Sizing Memory Allocation
Right-sizing Lambda functions involves setting memory from 128 MB to 10,240 MB. AWS allocates more CPU resources to functions with higher memory, which helps your function run more quickly. This saves cost on function duration as the function runs fast.
Performance Testing for Optimal Settings
The AWS Lambda Power Tuning tool helps test different memory configurations. It uses Step Functions to run your function with various memory settings. It measures cost and runtime.
Memory vs Execution Time Trade-offs
Adjusting memory settings involves balancing costs and execution time. Functions requiring significant computing power can operate more quickly with increased memory. This decreases the total amount you’re billed for.
Calculate your total cost per invocation by multiplying the memory cost by the execution time. For example, if you allocate 512 MB (0.5 GB) and the function runs for 1.5 seconds, that equals 0.75 GB-seconds × $0.0000166667 = $0.0000125 per invocation. The best memory setting is the one that reduces this total cost, not just the cost per second or the execution time.
2. Execution Time Optimization Techniques
Every millisecond your function runs increases your bill. Improving performance helps manage costs without compromising functionality. Focus on reducing your deployment package size and simplifying dependencies. Initialise SDK clients and database connections outside your handler function to save time between invocations.
Lazy Loading and Initialization
Lazy loading delays resource loading until needed, reducing cold start times. Only load big dependencies when your function needs them. This cuts down memory use and speeds up execution.
Start resources outside your handler to reuse containers. AWS Lambda containers stay active between calls, letting you reuse clients and connections.
Efficient Algorithm Implementation
Choose algorithms with the best time complexity for your task. Replace slow operations with faster ones when handling large data sets. Optimise data processing to minimise memory usage and garbage collection. Use streaming for large files instead of loading them all at once.
| Optimization Technique | Impact Level | Implementation Effort | Cost Reduction |
| SDK Client Initialization | High | Low | 20-40% |
| Algorithm Optimization | Medium | Medium | 15-30% |
| Lazy Loading | Medium | Low | 10-25% |
| Connection Pooling | High | Medium | 25-50% |
*Actual savings vary by workload.
3. Lambda Cost Optimization Through Cold Start Reduction
Reducing cold start delays can lower your Lambda expenses and enhance user satisfaction. Cold starts occur when AWS initiates new environments for your functions, leading to slower performance and increased costs. Implementing cold start reduction strategies helps you save money and ensures your functions perform reliably.
Provisioned Concurrency Implementation
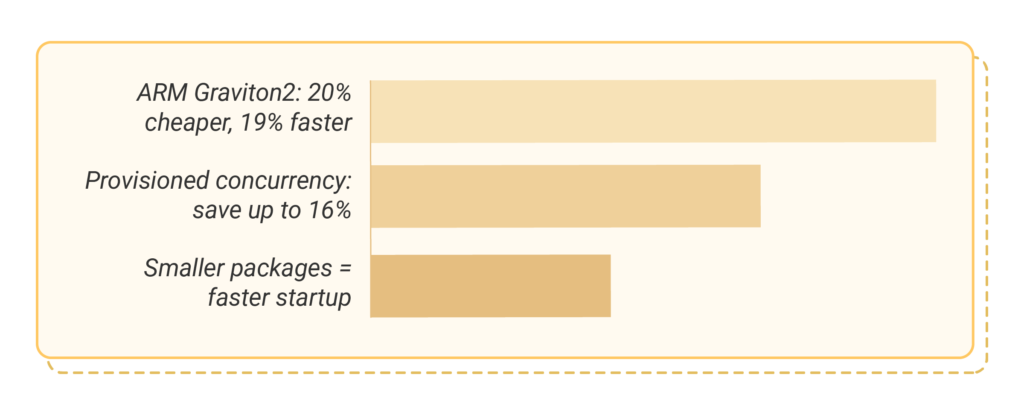
Provisioned concurrency keeps your functions ready to go without delay. It prevents cold starts for the specified capacity. If your functions are always busy, you can save up to 16% on costs. You still pay for provisioned concurrency even if your functions aren’t busy. Determine when it’s worth it by comparing costs. Functions with consistent traffic patterns gain the most benefits.
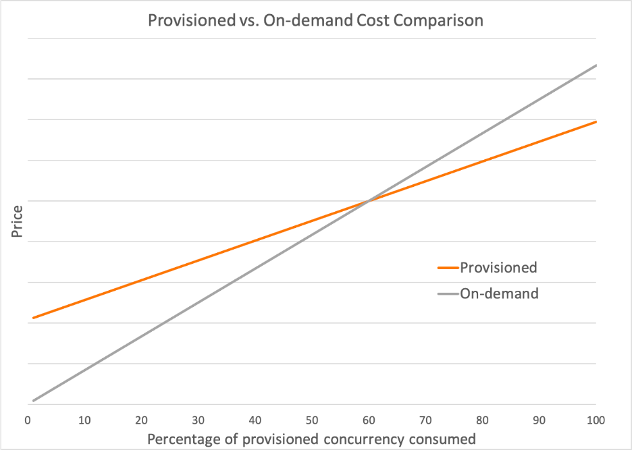
Source: AWS Blog – Optimizing your AWS Lambda costs
Runtime Selection Impact
Selecting the right runtime is crucial for quick starts and reduced costs. Using ARM-based Graviton2 processors can deliver 20% savings and offer 19% better performance than x86. Python and Node.js initialise more quickly than Java or .NET.
Package Size Optimization
Optimising package size helps your functions start faster. Smaller packages reduce the time AWS takes to download and unpack. Remove unused code, compress files, and utilise Lambda layers for shared code.
4. Database and External Service Optimization
Improving how your Lambda functions communicate with other services can reduce both time and cost. Optimising your database and improving service integration help lower your AWS bill, as you use less time and data.
Connection Pooling Strategies
Old methods of connecting to databases can slow down your Lambda functions. Connection pooling allows you to reuse the same connection for multiple calls. Set up connection pools outside your main function to keep connections open between calls. Use global variables to maintain them during warm starts.
RDS Proxy Implementation
Using RDS Proxy can reduce connection overhead by up to 66% by reducing failover. Your Lambda functions connect to the proxy, making them faster and cheaper.
API Call Efficiency
API calls can slow down your functions and increase costs. Cache frequently used data to reduce extra API calls. Use VPC endpoints for AWS services to minimise data transfer expenses. Implement exponential backoff for retries to avoid failures.
5. Event Source and Trigger Optimization
Your event architecture determines how frequently functions run and affects your AWS bill. It’s essential to ensure functions only execute when necessary.
Event sources like S3, DynamoDB, and SQS can cause excessive function calls if not managed properly. Each unnecessary call raises your costs without providing additional value. Optimising your triggers can reduce your Lambda expenses by 30-50%.
Efficient Event Processing
Using event filtering at the source level prevents functions from processing irrelevant events. AWS EventBridge and SQS allow you to filter messages to block unwanted calls before they reach your Lambda function.
Polling vs Push Event Models
Push-based event models like API Gateway and S3 triggers are more cost-effective than polling systems. They only invoke your function when events occur, avoiding unnecessary executions.
Polling optimisation is essential when using SQS or Kinesis as event sources. Use long polling to reduce empty receive requests that waste time. Select the appropriate polling intervals based on your app’s latency requirements.
6. Monitoring and Cost Alerting Setup
Implementing effective monitoring systems helps identify cost overruns early, allowing you to better manage expenses. You can see where your money is going and receive alerts when costs become excessive.
Using AWS tools together provides a comprehensive view of Lambda costs, enabling you to detect trends, identify anomalies, and keep spending under control.
CloudWatch Cost Monitoring Configuration
CloudWatch monitoring provides comprehensive insights into Lambda expenses. You can view the cost of each function, region, and time period. Create custom dashboards to display both costs and performance together.
Use cost allocation tags to categorise expenses by project, environment, or team. These tags assist you in identifying which functions utilise the most resources. Create customised metrics to combine cost data with the frequency of function usage.
Automated Budget Alerts
AWS Budgets allows you to set spending limits that send alerts when reached. Set budget alerts at 50%, 80%, and 100% of your monthly budget. These alerts notify you early so you can respond quickly.
Create budget alerts for different cost categories, like development, staging, and production. This detailed approach helps you keep expenses in check throughout every stage of your app’s lifecycle.
Take Control of Your Lambda Costs Today
Managing AWS Lambda costs can feel overwhelming, especially when hidden inefficiencies and underutilized resources quickly add up. Elite Cloud helps you cut through the complexity with a free cost assessment that uncovers immediate savings opportunities.

Don’t leave your cloud budget at risk. Contact Elite Cloud today and start optimizing your AWS environment with confidence.




