Managing your AWS DynamoDB cost is essential for keeping your cloud expenses in check. Companies like Netflix, Disney+, Zoom, Dropbox, Nike, and Capital One rely on it for their critical applications. This guide shares top strategies for cloud cost control. You’ll learn how to reduce costs without sacrificing performance or reliability.
Understanding DynamoDB Pricing Models and Cost Components
DynamoDB’s pricing structure includes capacity charges, storage fees, and additional service fees. Understanding these components helps you make informed choices about your database setup.
On-Demand vs Provisioned Capacity Pricing
DynamoDB provides two different capacity modes that decide how you are billed for database operations.
On-demand capacity mode charges only for the actual read and write requests your application makes. This model automatically scales to handle traffic changes without the need for capacity planning.
Provisioned capacity mode requires you to specify the number of reads and writes per second your application needs. You pay for the capacity you reserve, regardless of actual usage. This model provides predictable costs and lower per-request pricing for consistent workloads.
Storage Costs and Data Transfer Fees
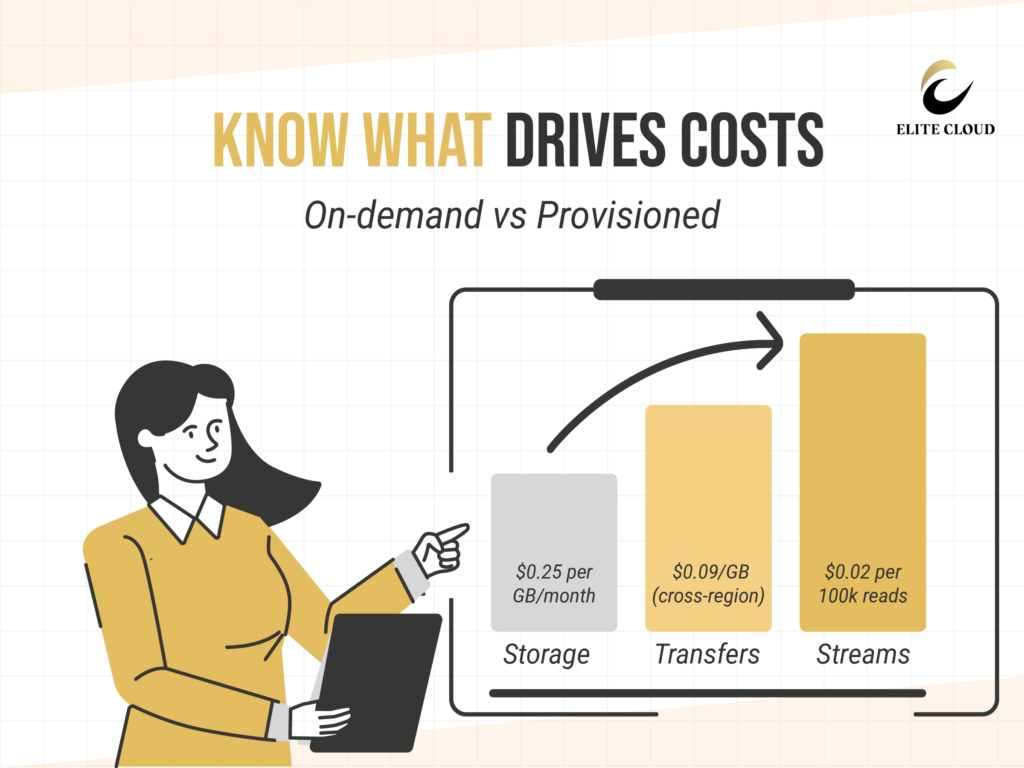
Storage costs apply to all data stored in your DynamoDB tables, regardless of your chosen capacity mode. AWS charges $0.25 per GB per month for extra storage (varies by region). These costs cover your table data, local secondary indexes, and global secondary indexes.
Data transfer fees apply when moving data between AWS regions or from DynamoDB to the internet. Transfers within the same AWS region are free. Cross-region transfers cost $0.09 per GB for the first 10 TB each month. Internet data transfer rates vary depending on the destination and volume.
Additional Service Charges and Hidden Costs
Several optional DynamoDB features incur extra charges beyond basic capacity and storage costs. Global Tables replicate your data across multiple regions, increasing write capacity usage and incurring cross-region transfer fees. DynamoDB Streams track data changes and cost $0.02 per 100,000 stream read requests.
Backup and restore operations incur additional charges beyond your regular database costs. On-demand backups are priced at $0.10 per GB per month for storage.
1. Efficient Data Modeling for Cost Reduction
The design of your table impacts read and write costs, storage, and performance. Making informed choices early can prevent expensive adjustments later.
Single Table Design Principles
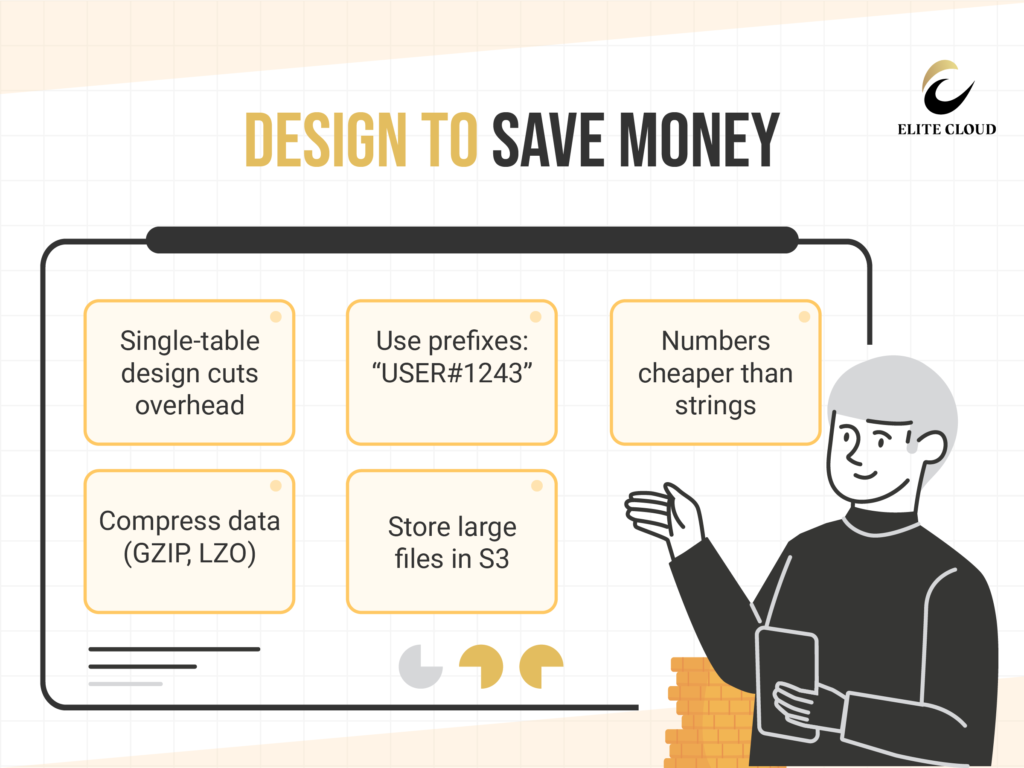
Single table design merges multiple entity types into one table, reducing costs and overhead. Instead of separate tables for users, orders, and products, all data is stored together. Use prefixes to distinguish entity types, like “USER#1243” for users and “ORDER#456” for orders. This helps keep data organized and improves query efficiency.
Optimizing Attribute Selection and Data Types
Optimizing attributes impacts storage costs and query performance. Each byte in DynamoDB contributes to your bill, so select the most compact data types. Use the smallest data types that still fulfill your app’s requirements.
Strings use more space than numbers. Use numbers for identifiers and status codes whenever possible. Replace lengthy text with numeric codes that link to full descriptions in your app.
Large values or images can rapidly raise costs. Use compression methods like GZIP or LZO to reduce item sizes. Store large objects in Amazon S3 and utilize DynamoDB for object identifiers.
Composite Keys and Access Pattern Design
Composite keys optimize data retrieval and reduce costs by using smart access patterns. Your partition and sort keys should align with your most common query patterns. This minimizes the need for costly scans and secondary indexes.
Design composite keys for hierarchical data. Use sort keys for range and prefix matching. For example, “2024-01-15#ORDER#123” supports queries by date, type, and specific identifiers.
Designing access patterns involves understanding how your app retrieves data. Determine your query requirements before setting up keys. Each pattern should utilize the primary key or a well-crafted Global Secondary Index (GSI).
2. Implementing Auto Scaling for Dynamic Workloads
Auto Scaling Configuration Best Practices
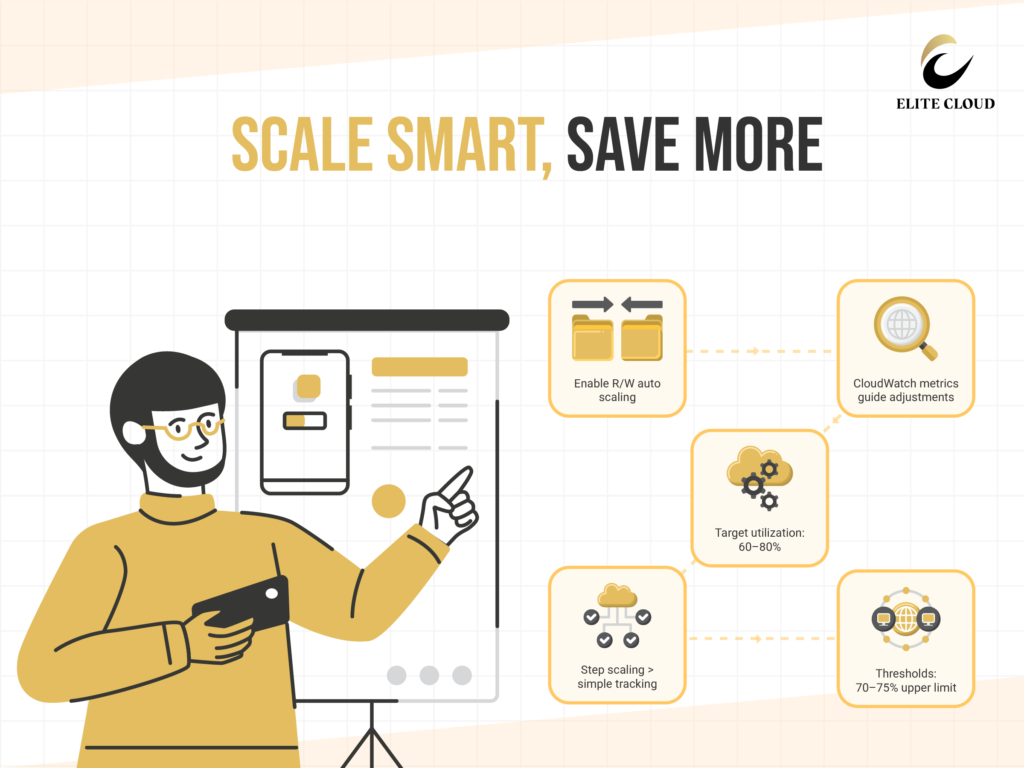
Setting up auto scaling correctly is important. Enable it for both read and write capacity. Set a minimum capacity for basic traffic and a maximum based on your budget.
Target Utilization and Scaling Metrics
Target utilization influences costs and performance. Aim for 60-80% for most applications. Higher rates may lead to throttling, while lower rates result in wasted money.
CloudWatch metrics inform scaling decisions. Use ConsumedReadCapacityUnits and ConsumedWriteCapacityUnits; these indicate when to adjust capacity.
Custom Scaling Policies and Thresholds
Custom policies allow precise control of scaling. Use step scaling for detailed adjustments, which is more effective than simple target tracking. Setting thresholds is essential. Set upper thresholds at 70-75% to prevent performance drops, while lower thresholds should accommodate natural traffic fluctuations.
3. Storage Optimization and Data Lifecycle Management
Proper item sizing, compression, and automated data expiration can significantly reduce your DynamoDB storage costs. Using smaller item sizes lowers storage expenses, and shorter attribute names cost less too. For example, replace “customer_identification_number” with “custId.”
Choose data formats that require less space. Use epoch timestamps for dates instead of ISO strings. Epoch timestamps are just 10 digits, while ISO strings are 24 or more.
Data Compression and Encoding Methods
Data compression can make items much smaller before they’re stored in DynamoDB. GZIP can shrink text data by 60-80%. LZO is faster but compresses less.
Apply compression before writing items to DynamoDB. This means you’ll need to decompress during reads. But it saves a lot of money on storage for big items.
Time-to-Live Implementation Strategies
TTL implementation automates data cleanup at no extra cost. DynamoDB’s TTL feature removes items when they expire, operating continuously. To enable TTL, add a numeric attribute with the expiration timestamp. DynamoDB deletes items within 48 hours of the specified time. Plan your TTL based on your data retention needs.
4. Reserved Capacity Planning and Purchase Strategies
DynamoDB reserved capacity can significantly cut costs for companies that understand their database requirements. Committing to a specific capacity level grants substantial discounts. It’s important to use reserved capacity wisely to save money over the long term.

When Reserved Capacity Makes Financial Sense
Reserved capacity is a great option when your DynamoDB usage is steady and long-term. It’s ideal for apps with consistent traffic, like content sites or login services. This can help you save a lot of money.
| Reservation Term | Upfront Payment | Effective Savings Potential* |
| 1 Year | Any (partial or full) | Up to 54% off standard provisioned rates |
| 3 Year | Any (partial or full) | Up to 77% off standard provisioned rates |
Source: Amazon DynamoDB Pricing, Reserved Capacity (accessed September 2025).
5. Global Tables and Multi-Region Cost Management
DynamoDB Global Tables provide powerful multi-region capabilities. However, managing costs across regions requires careful planning. When you use global tables, you create multiple data copies in different AWS regions. This setup ensures disaster recovery and quick access for users worldwide.
Multi-region costs can increase without proper planning. Each region has its own expenses for reading and writing, storage, and network transfers. Understanding these costs helps you design your global setup effectively.
Before implementing global tables, determine if the costs are justified. You might discover cheaper options such as backups or manual replication for less critical data.
6. Backup, Recovery, and Archive Cost Strategies
Smart backup and recovery strategies can reduce your DynamoDB storage costs. You can save significantly by using AWS’s tiered storage and lifecycle management.
Point-in-Time Recovery Cost Management
Point-in-time recovery keeps your data safe, but managing costs is important. You pay for the storage of change data during the backup period. This can add up, especially for tables with many updates. Adjust your backup retention period based on your needs. Shortening retention from 35 days to 7 days can reduce monthly costs.
On-Demand Backup Optimization
On-demand backups have predictable costs but require smart scheduling to save money. Develop backup policies that align with your data change patterns and business requirements. AWS Backup’s cold storage tier can reduce long-term backup storage expenses by up to 66%, as it automatically shifts older backups to more affordable storage.
Long-Term Data Archiving to Amazon S3
Data archiving to Amazon S3 is the most cost-effective way to store data long-term. You can export DynamoDB data to S3, which is cheaper than storing it in DynamoDB. Use S3’s tiering and lifecycle policies to reduce archiving costs. Data stored in S3 Glacier or Deep Archive costs up to 80% less than DynamoDB, while still remaining accessible for compliance and analytics.
7. Monitoring and Alerting for Proactive Cost Control
Effective cost control requires real-time monitoring of your DynamoDB expenses. Without clear visibility, you could encounter unexpected budget overruns. Cost monitoring helps identify trends and anomalies, guiding your DynamoDB resource usage.
Set up alert levels for different scenarios. Use warning alerts at 75% of your budget and critical alerts at 90%. This approach prevents alert fatigue while ensuring you catch important cost increases.
Unlock Big Savings on Your DynamoDB Costs
DynamoDB’s speed and scalability are unparalleled, but without proper cost strategies, expenses can quickly spiral out of control. Underutilized capacity, inefficient queries, and hidden service charges often drain the biggest portion of the budget.

At Elite Cloud, we help businesses like yours identify inefficiencies and unlock significant savings, all while maintaining performance. Get started with a free AWS cost assessment today, and see exactly where you can reduce costs and maximize DynamoDB’s value.